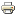
CG-4 glider being towed into air by a Douglas C-47 Skytrain.
Gliders were lightweight, engineless airplanes towed by cables into the skies by much bigger, motored aircraft, then released to cruise quietly and often undetected by enemy troops.
They required less training for troops than parachuting, and were effective on nighttime missions. The CG-4 glider could carry 13 troops and their equipment or a jeep, a quarter-ton truck or a 75mm howitzer.
 Jeep being unloaded from a military CG-4 glider at the Victorville Army Flying School, Victorville, CA. circa 1943.
Jeep being unloaded from a military CG-4 glider at the Victorville Army Flying School, Victorville, CA. circa 1943.
California played a prime role in the development of the glider fleet. Beginning in 1941, pilots trained at airfields in the Mojave Desert, including the Victorville Army Air Field (later designated George Air Force Base) and Twentynine Palms (now the Marine Corps Air Ground Combat Center).
The downside to the military glider was that it lacked maneuverability in the air, and despite being equipped with landing gear, many crashed—it was often referred to as the “Flying Coffin.”
 Profile of an Army Air Force CG-4 glider waiting on runway for a tow.
Profile of an Army Air Force CG-4 glider waiting on runway for a tow.
“Without engines, the gliders had little ability to change course to avoid obstacles or harsh terrain,” historian Carolyn Apple wrote. “The goal was to land the gliders, without significant damage to the cargo or crew, in open terrain that was close enough to the enemy. Unfortunately, glider pilots were killed at a higher rate during both training and assigned missions. The gliders would often be destroyed during landing.”
By the time World War II ended, more than 14,000 gliders and their crews helped the Allies win the war. The Army ended its use on January 1, 1953. However, the U.S. Air Force continues to use sailplanes at the Air Force Academy to train cadets in the fundamentals of flight.
For more information, read historian Mark Landis’ piece about the development of the glider program in the Mojave Desert during World War II.
Source: CalVet