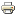
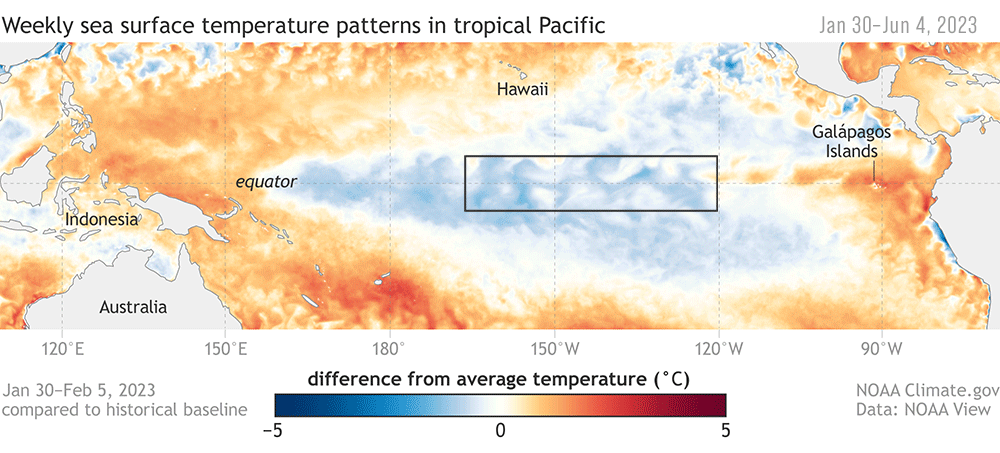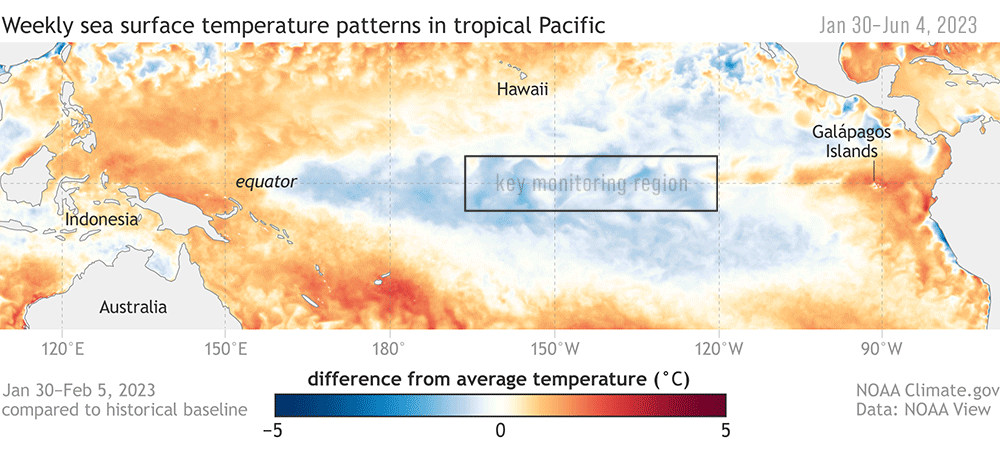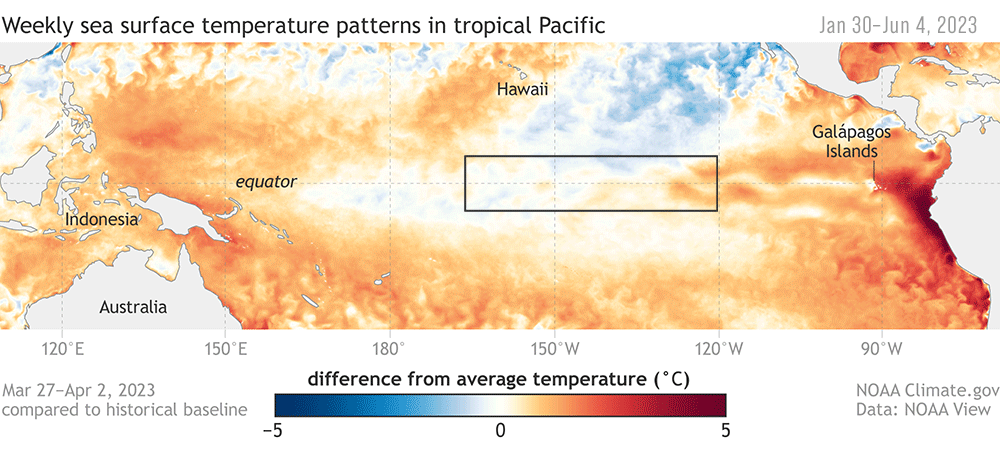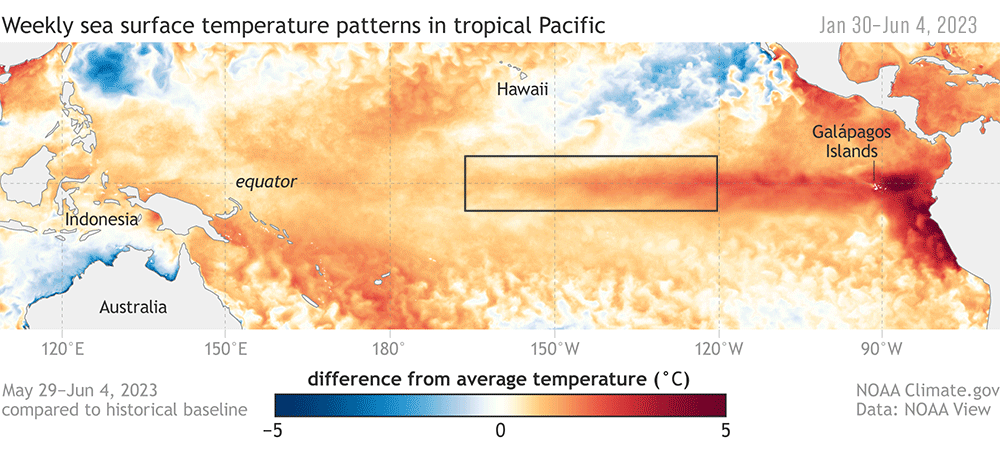
Animation of maps of sea surface temperatures in the Pacific Ocean compared to the long-term average over five-day periods from the end of January to early June 2023. The waters in the key monitoring region, which scientists call "the Niño-3.4 region," start out cooler than average (blue) and progressively become warmer than average (red) as La Niña ends and El Niño arrives. A higher-resolution version of this animation is available as a movie. NOAA Climate.gov, based on Coral Reef Watch maps available from NOAA View.
June 11, 2023 - The expected El Nino has emerged, according to scientists at NOAA’s Climate Prediction Center, a division of the National Weather Service. In the monthly outlook released last week, forecasters issued an El Nino Advisory, noting that El Nino conditions are present and are expected to gradually strengthen into the winter.
El Nino is a natural climate phenomenon marked by warmer-than-average sea surface temperatures in the central and eastern Pacific Ocean near the equator, which occurs on average every 2-7 years. El Nino’s impacts on the climate extend far beyond the Pacific Ocean.
"Depending on its strength, El Nino can cause a range of impacts, such as increasing the risk of heavy rainfall and droughts in certain locations around the world," said Michelle L'Heureux, climate scientist at the Climate Prediction Center. "Climate change can exacerbate or mitigate certain impacts related to El Nino. For example, El Nino could lead to new records for temperatures, particularly in areas that already experience above-average temperatures during El Nino.”
El Nino’s influence on the U.S. is weak during the summer and more pronounced starting in the late fall through spring. By winter, there is an 84% chance of greater than a moderate strength El Nino, and a 56% chance of a strong El Nino developing. Typically, moderate to strong El Nino conditions during the fall and winter result in wetter-than-average conditions from southern California to along the Gulf Coast and drier-than-average conditions in the Pacific Northwest and Ohio Valley. El Nino winters also bring better chances for warmer-than-average temperatures across the northern tier of the country.
A single El Nino event will not result in all of these impacts, but El Nino increases the odds of them occurring.
The anticipated persistence of El Nino also contributed to the 2023 Atlantic and Eastern Pacific Hurricane Outlooks issued by NOAA last month. El Nino conditions usually help to suppress Atlantic Hurricane activity, while the presence of El Nino typically favors strong hurricane activity in the central and eastern Pacific Basins.
The Climate Prediction Center’s seasonal temperature and precipitation outlooks will continue to take into account current and forecasted El Nino conditions. These seasonal outlooks are updated monthly, with the next update on June 15. The Atlantic Hurricane Season Outlook will be updated in early August.
Scientists have been forecasting the development of El Nino for the last few months and issued the first El Nino Watch on April 13. 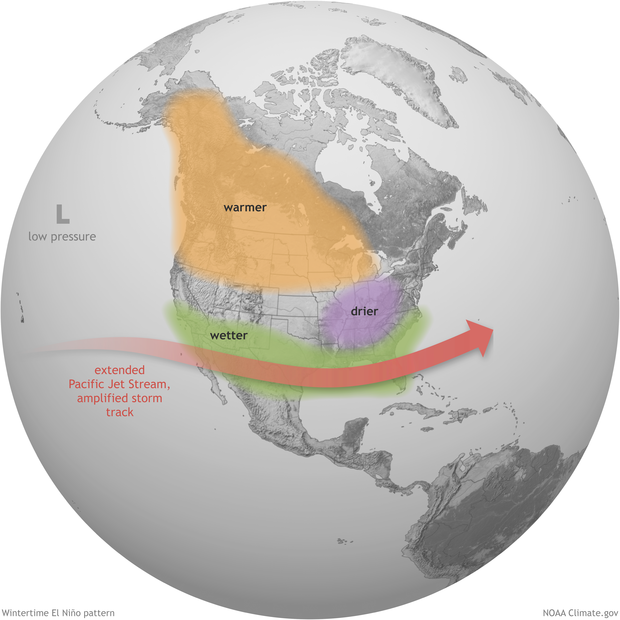
Source: NOAA