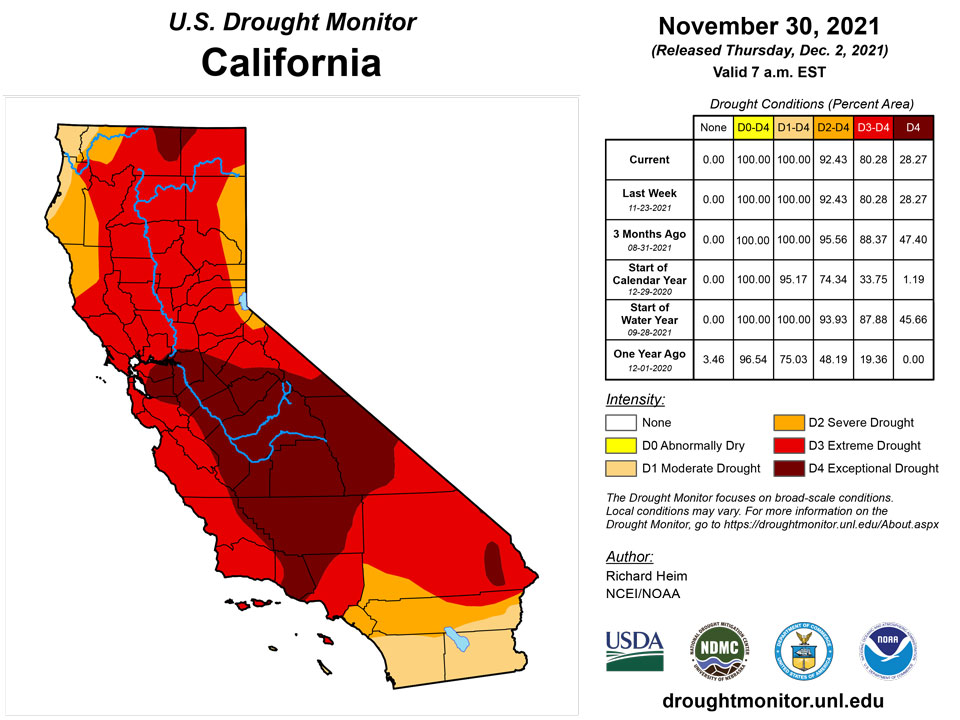
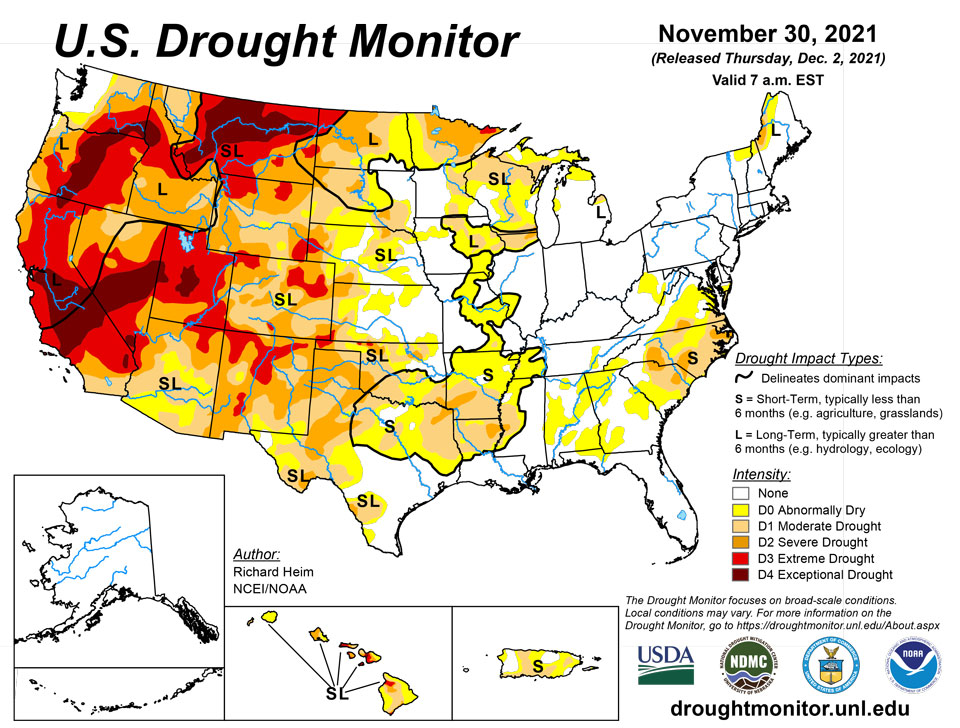
California and National Drought Summary for November 30, 2021
Summary
December 2, 2021 - Several Pacific weather systems moved across the contiguous U.S. (CONUS) during this U.S. Drought Monitor (USDM) week. An upper-level ridge over the western CONUS directed the systems across the northern states, while a cutoff low trekked across Texas then into the Gulf of Mexico. The Pacific systems dragged cold fronts with them that stretched the width of the CONUS, from the Great Lakes to the Gulf of Mexico coast. The fronts triggered rain and snow over parts of the country, but they were starved of precipitation by the western ridge and its northwesterly flow over the central CONUS. As a result, the week was wetter than normal only in parts of the Pacific Northwest, northern Rockies, Great Lakes, and Texas. The weather was drier than normal across the rest of the CONUS with large parts of the West, Great Plains, Upper Mississippi Valley, and Southeast receiving no precipitation. Most of the West and Great Plains were warmer than normal thanks to the western ridge. The persistent above-normal temperatures contributed to excessive evapotranspiration in western portions of the Great Plains as well as parts of the West, as seen in EDDI and ESI indicators. Lack of precipitation, excessive evapotranspiration, and windy conditions further dried soils, again especially in western portions of the Plains, as seen in several soil moisture indicators. Drought indicators such as the Standardized Precipitation Index (SPI) and Standardized Precipitation Evapotranspiration Index (SPEI) reflected the mounting precipitation deficits. The continued dryness expanded or intensified drought in parts of the southern to central Rockies, Great Plains, Lower to Mid-Mississippi Valley, Southeast, and Mid-Atlantic states, as well as Puerto Rico.
Northeast
Parts of New York, Pennsylvania, and northern New England received half an inch to locally an inch of precipitation this week while southern portions had less than half an inch. No change was made to the moderate to severe drought that lingered in northern New England, but short-term dryness and low streamflows prompted expansion of abnormal dryness in West Virginia.
Southeast
By the time the cold fronts reached the Southeast, the only precipitation they could muster was less than half an inch and that was only in parts of northern Alabama. The rest of the region had little to no precipitation. With dryness intensifying over the last 3 months and soils continuing to dry, abnormal dryness and moderate drought expanded, and areas of severe drought developed, in the Carolinas and Virginia. Abnormal dryness grew in Alabama and Georgia and developed in the Florida panhandle. According to November 28 U.S. Department of Agriculture (USDA) statistics, topsoil moisture was short or very short (dry or very dry) for 55% of South Carolina, 54% of North Carolina, 46% of Georgia, 28% of Virginia, 26% of Florida, and 22% of Alabama. These were all 5 to 12% more than a week ago.
South
Half an inch to 1.5 inches of rainfall was widespread across coastal to eastern Texas, and into adjacent parts of Louisiana, and locally over 2 inches fell over parts of Texas. Smaller swaths of half an inch of rain occurred over north Texas and parts of Arkansas, Mississippi, and Tennessee. But the rest of the region had less than half an inch, with much of western Texas to most of Oklahoma receiving little to no precipitation. Moderate to severe drought contracted in a few parts of Texas where the heaviest rains fell, but much more of the state, as well as parts of Oklahoma, Arkansas, and Louisiana, saw expansion of abnormal dryness and moderate to severe drought. Areas of abnormal dryness expanded in western Tennessee and developed in eastern portions of the state. With every passing day of no precipitation, low humidity, high evapotranspiration, the wildfire threat continued to grow in Texas and Oklahoma. According to November 28 USDA statistics, 64% of the topsoil moisture in Texas was short or very short (dry to very dry) and 45% of the winter wheat crop was in poor to very poor condition. In Oklahoma, the statistics were 59% for topsoil moisture and 16% for winter wheat condition.
Midwest
Half an inch of precipitation fell across the Great Lakes and parts of Missouri to the confluence of the Mississippi and Ohio Rivers, with less than half an inch across the Ohio Valley states and little to no precipitation over the Upper Mississippi Valley. Reassessment of the last 2 months’ precipitation led to deletion of extreme drought over the Lake of the Woods region, contraction of moderate to severe drought in northwest Minnesota, and contraction of extreme drought in the northeast part of the state. But abnormal dryness expanded in parts of Illinois, Missouri, and southeast Iowa where 30-day dryness intensified and soils continued to dry.
High Plains
Little to no precipitation fell across the High Plains region this week. Reassessment of the last 2 months’ precipitation led to contraction of moderate drought in northeast North Dakota and severe drought in the central part of the state. But water levels in ponds and dugouts remained low in spite of late summer to early fall rains, thus prompting expansion of severe drought in other parts of central North Dakota. Above-average temperatures and no precipitation for the last 2 weeks resulted in expansion of moderate drought in southern parts of North Dakota and adjacent South Dakota. In Wyoming, many basins had below to well below normal snowpack with no snow across the High Plains portion of the state, and snow, where it has occurred, was confined to the highest peaks (above 8500 ft). The snow conditions combined with excessive evapotranspiration, drying soils, short-term dryness, and longer-term dryness to prompt expansion of moderate to extreme drought in parts of the state. In Colorado, drying soils, high evapotranspiration, low mountain snowpack, and mounting precipitation deficits resulted in expansion of moderate to extreme drought in many parts of the state. November 28 USDA statistics had 84% of Colorado’s topsoil short or very short of moisture and 33% of the winter wheat in poor to very poor condition. Abnormal dryness and moderate drought expanded in southern and western parts of Kansas.
West
Pacific weather systems brought 0.5-3.0 inches of precipitation to coastal portions of Oregon and Washington, with 5 inches or more falling in non-drought areas of northwest Washington. Half an inch to locally 2 inches also fell over parts of the northern Rockies, while locally up to half an inch occurred over a few parts of the southern Rockies. Otherwise, much of the West was dry. Drying soils and mounting 3-month precipitation deficits prompted expansion of moderate to extreme drought in parts of New Mexico. November 28 USDA reports had 81% of New Mexico’s topsoil short or very short of moisture. Otherwise, no change occurred to the vast areas of moderate to exceptional drought which covers the West.
Caribbean
The week was drier than normal in Puerto Rico. Moderate drought expanded in Puerto Rico where soils continued drying, stream levels were low, and 1-3 month rainfall deficits continued to mount.
The U.S. Virgin Islands remained dry for another week, at the end of a three month stretch that is typically the wettest for the region. Drought status did not change from the previous week with St. Thomas at D1-S (moderate drought), St. John at D0-S (abnormal dryness), and St. Croix at D2-SL (severe drought). With conditions being very dry on all islands, deterioration in drought condition is possible next week.
St. Thomas received 0.10 to 0.5 inches of rain over much of the island with a swath of rainfall yielding up to an inch across the midsection of the island, according to the National Weather Service’s Quantitative Precipitation Estimates for the past 7 days. St. John and St. Croix each received 0.25 inches or less over most of the islands.
St. John remained at D0-S. The Windswept Beach CoCoRaHS station reported 0.27 inches, which is below normal. Other CoCoRaHS stations reported 0.40 inches or less. The SPI values for Windswept Beach range indicate no dryness at 3 and 6 months, abnormal dryness at 9 months, moderate drought at 12 months, and severe drought at 1 month, and averaging to abnormal dryness. The Susannaberg DPW 3 Well was about 15.34 feet below the land surface, which is quite low.
St. Croix remained at D2-SL. Precipitation at Henry Rohlsen AP amounted to 0.11 inches, which is below normal. The CoCoRaHS stations reported 0.31 inches or less. The SPI values for Henry Rohlsen AP indicate extreme drought at 1 month, severe drought at 3, 9 and 12 months, and moderate drought at 6 months, and averaging to severe drought. The Adventure 28 Well was at 28.26 feet below land surface on Nov. 30, edging very close to its lowest recorded level, which occurred on Oct. 31-Nov. 1, 2016, when the depth to water was 28.32 feet.
St. Thomas remained at D1-S. Precipitation at Cyril E. King AP was 0.21 inches, or below normal. The CoCoRaHS stations reported 0.40 inches or less. The SPI values for the King Airport indicate moderate drought at 1 and 12 months, severe drought at 3 months, and abnormal dryness at 6 and 9 months, and average to moderate drought. The Grade School 3 Well was at 13.78 feet below land surface on Nov. 30, which is quite low for the well.
Pacific
The week was drier than normal in Hawaii. The depiction was unchanged in Hawaii.
The week was drier than normal in most of Alaska, with wetter-than-normal conditions in the Alaska panhandle. Alaska remained free of drought and abnormal dryness.
The Republic of Palau was free of dry conditions and received 3.24 inches at Palau IAP and 2.03 inches at Koror COOP.
The Mariana Islands also remained free of dryness. Rainfall at all locations exceeded the 1-inch weekly minimum to satisfy water needs. Guam and Rota received 4.54 inches and 3.82 inches, respectively. Saipan rain amounts ranged from 2.60 inches to 3.27 inches.
The Federal States of Micronesia were largely free of drought, apart from Kapingamarangi, which was entering its second week of extreme (D3) drought. A report from Kapingamarangi via WSO Pohnpei indicated that recent rainfall helped catchment tank levels. The community water tanks were nearly 100% full and private (personal) water tanks were around 50% full. Vegetation was still stressed and yellowing.
Several other locations in Micronesia had 2 inches or more, which is adequate for weekly water needs. Chuuk received 3.23 inches; Pingelap, 4.41 inches; and Pohnpei, 4.34 inches. A few other locations, like Fananu, Kosrae, Lukunor, Nukuoro, Ulithi, and Yap received less than 2 inches, but received enough rainfall in previous weeks that water supplies should not yet be a concern. Woleai had 4 days’ worth of data missing, so this location was set to no data for the week, although adequate rain in recent weeks should mean that there is enough water to meet needs.
The Marshall Islands continued to be wet with most locations receiving more than 2 inches of rain, or enough to satisfy weekly water needs. Ailinglaplap reported 8.12 inches and Mili got 4.63 inches, while other locations received more than 2 inches. The Majuro reservoir, which has a maximum capacity of 36 million gallons, held 27,314 million gallons on Nov. 29.
American Samoa remained free of dry conditions. Rainfall for Pago Pago was 3.40 inches, Siufaga Ridge reported 1.80 inches, and Toa Ridge received 1.62 inches.
Looking Ahead
The upper-level ridge will dominate the weather over the western CONUS for the first half of the next USDM week, with a couple Pacific frontal systems moving in later in the week. For December 2-7, the fronts will bring an inch to locally 3 inches of precipitation to parts of coastal Washington and Oregon and the northern Rockies, with 1 to 2 inches in a wide swatch from eastern Oklahoma to the southern Appalachians and north across the Ohio Valley to parts of New England. Half an inch to an inch will spread from the swath to the central Gulf of Mexico coast and across the Great Lakes. Most of the Plains and Southwest, as well as much of Virginia, the Carolinas, and Florida, will receive little to no precipitation. Temperatures are expected to average warmer than normal across most of the CONUS during this period. For December 7-15, odds favor above-normal precipitation across the West and Ohio Valley, with lesser chances for above-normal precipitation in the northern Plains and along the East Coast. Odds favor near to below-normal precipitation in the southern Plains and southern Florida. Much of Alaska is likely to be wetter than normal. Odds favor warmer-than-normal temperatures across most of the CONUS, with near to below-normal temperatures in the Pacific Northwest and early in the Great Lakes. Alaska is likely to be colder than normal, especially in southern portions of the state.
Author(s):
Richard Heim, NOAA/NCEI
Denise Gutzmer, National Drought Mitigation Center
Dryness Categories
D0 Abnormally Dry—used for areas showing dryness but not yet in drought, or for areas recovering from drought.
Drought Intensity Categories
D1 Moderate Drought
D2 Severe Drought
D3 Extreme Drought
D4 Exceptional Drought
Drought or Dryness Types
S Short-term, typically less than 6 months (agriculture, grasslands)
L Long-term, typically more than 6 months (hydrology, ecology)
SL Area contains both short- and long-term impacts
Source: National Drought Mitigation Center